Content
Protecting against pests, including fighting currant glass, is an indispensable component of competent care for this horticultural crop. Glassy is an insect that can not only damage the plant, reduce its yield, but also cause its death. A set of preventive measures and the use of special tools will help solve this problem.
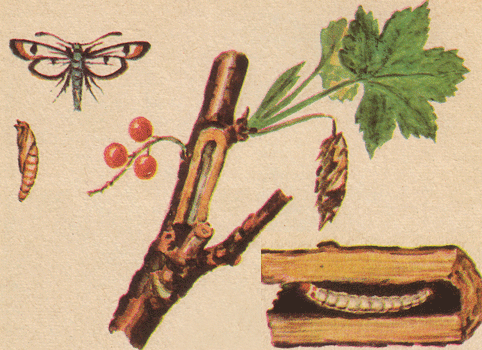
Signs of a currant glass
Currant glass is an insect that looks like a wasp and belongs to the family of butterflies. Its characteristic features:
- an oblong body covered with dark scales, up to 1 cm long;
- light yellow stripes on the abdomen: 3 - in the female, 4 - in the male;
- thin transparent, like glass, wings with black veins and a narrow orange border along the edges, reaching a span of 22 - 28 mm.
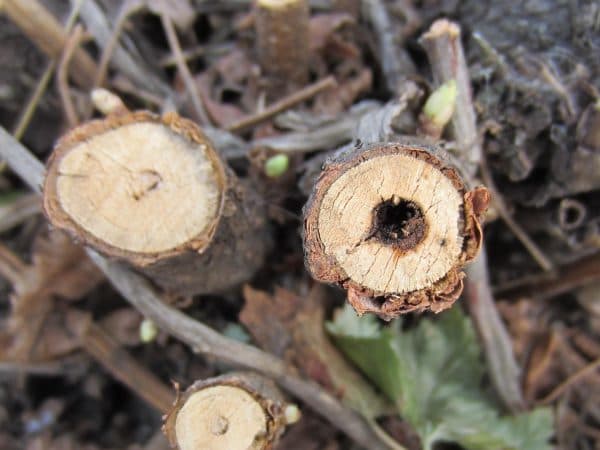
The photo shows the described signs of a glass case on a bush.
The basis of the glass jar nutrition is sap and pollen of plants. In late May - early June, females lay up to 50 - 60 eggs of the correct oval shape. For laying, they use notches and microcracks in the bark of treelike shoots of currants, gooseberries, raspberries, choosing a place closer to young buds.
For horticultural crops, including currants, glassy larvae are dangerous. They are caterpillars 2 - 2.5 cm long, light beige or white with a dark head. Starting from the 10th day after emergence, they penetrate deep into the shoots, develop and feed there. Gradually, they go to the base of the branch, completely destroying its core. By the spring of the second year, the larva emerges from the shoot at the soil surface, turns into a pupa, and then, in June, when the temperature is above 15 degrees Celsius, into a butterfly, which can lay eggs on the same bush. Thus, the number of larvae increases. These are young individuals that have settled in new increments, as well as individuals of the last year, living in stiff branches. Thus, some specimens develop in a one-year cycle, and some in a two-year cycle. The active life of the glass case lasts 40 - 42 days, the mass years lasts up to 10 - 18 days and ends by the ripening period of the currant berries. The life span of the insect is 2 years.
What is the danger of a glass case for currants
The glass pot is dangerous for black and red currants. In the first year of defeat by this pest, diseased branches do not outwardly differ from healthy ones. But gradually the first signs of bush diseases appear:
- a sharp decrease in the size of berries and leaves on the shoot;
- wilting of a bush that has not yet bloomed;
- few peduncles and poor quality of the ovary;
- dropping unripe berries;
- the growth of shoots by autumn is less than 15 cm;
- the most informative sign of a lesion with a currant glass is a darkened, almost black, core with a hole in the central part;
- on the longitudinal section of the damaged branch, a passage is visible, partially filled with excrement, and sometimes a caterpillar can be found in it;
- at the base of the branches, in the places where butterflies emerge, for several days you can observe the skin of the pupae, which is then blown away by the wind or removed by precipitation.
The next year after the plant is infected with the pest, the currant branches begin to dry out. By this time, the glassy larva, having completely ejected the shoot from the inside, descends to its base and comes out to the surface. If you do not take drastic measures, the currants will die.
In warm weather, the glass can damage almost the entire berry in a short time. The foliage of the shrubs begins to wither gradually, the branches dry out and break off, their inner tissues turn into dust.
Protection of currants from glass pan is complicated by a number of reasons:
- long periods of colonization of the pest;
- mild initial symptoms of damage;
- the hidden presence of larvae in the tissues of the bush;
- the presence in one generation of individuals that develop in both annual and biennial cycles.
To the greatest extent, the glass case damages the black currant. In perennial plantings, 10 - 50% of the shoots are damaged by this pest. Red and white currants are less susceptible to the invasion of this insect - up to 10 - 30% of the branches. Due to the currant glass, the annual shortage of berries is 3 - 7 kg per hundred square meters.
Means for dealing with currant glass
It is possible to fight against glass on bushes of black, red, white currants using biological, chemical, agrotechnical methods.
A means of detecting the appearance of glass butterflies during their summer is the installation of traps. To this end:
- place in the crown of a bush container with a solution of fermented currant jam in water (1: 1);
- light traps are hung at the height of the crown in the form of sheets of cardboard, plywood or Whatman paper painted in bright colors (yellow, pink, orange), and troughs with syrup are placed under them.
Insects, attracted by the color or smell of the trap, fall into the sugar solution and die. By the number of individuals in the container, it is concluded that it is necessary to protect the currants from the glass.
More information about the fight against glass in a live example - in the video:
Chemical
The use of chemicals - insecticides - gives positive results in the fight against glass. They are only effective in direct contact with insects. The caterpillar inside the shoot will not be affected by the funds. The table shows the characteristics of some chemicals for the destruction of currant glass. They are consumed in the amount of 1 - 1.5 liters per shrub. They have a high impact speed: insects die within 1 - 3 hours.
A drug | Characteristic | Preparation of a solution in water | Recommendations for the processing of currants from the glass |
Kapbofoc | Universal plant protection against ticks and insects. | 30 g per 4 l | Process 2 times at intervals of 2 weeks. |
Kemiphos | The insecticide is similar to Kapbofos in its spectrum of action. | 5 ml per 5 l | Apply only fresh solution during the initial growing season. |
Fufanon | A drug based on organophosphorus with a universal action. | 10 mg per bucket | Process up to twice a season. |
Trichlometaphos-3 | Contact organophosphate insecticide of systemic action. Destroys the larvae, pupae of the glass pot on the soil surface. | 10 g per 5 l | • Spray the soil around the currant bush before flowering; • Consumption of funds 2 - 5 liters per 1 m2; • Frequency of processing -1 every 2 - 3 weeks. |
Kinmix | An effective preparation for fighting insects and their larvae. | 4 ml per 10 l | • Spray before and after flowering; • The period of validity is more than 3 weeks. |
Spark M | Low-toxic contact agent for the control of sucking and gnawing insects, partially fumigating. | 5 ml per 5 l | • Spray plants in the morning or evening in calm, windless weather; • 1 - 2 treatments per season; • Validity period - from two weeks. |
Biological
Biological preparations for the treatment of currants from glassy have the same mechanism of action as chemical insecticides. But they do not accumulate in berries and do not cause the death of beneficial soil microflora. Their disadvantage is the low, in comparison with chemical agents, the rate of exposure to pests.
High efficiency in destroying glassware is possessed by:
- Fitoverm (2 mg per 1 l);
- Bitoxibacillin (50 g per 5L);
- Spark Gold (5 ml per 10 l).
The crown of the currant bush and the trunk circle are treated with solutions of biological products. The optimal processing time is the end of May - June, during the period when the glassy larvae have already appeared, but have not yet managed to penetrate into the shoots. The treatment is carried out 2 - 3 times every two weeks, the consumption of the solution is 0.5 - 1.5 liters per bush.
Folk
The essence of folk methods of dealing with currant glass is the use of intense odors that repel the pest. Proven methods:
- plant crops with a strong odor between the rows of currants, such as garlic, onions, tomatoes, calendula, marigolds;
- plant an elderberry bush next to the berry, which has an unpleasant aroma for the glass, or you can hang its inflorescences on the currants;
- avoid the neighborhood of currants with bird cherry, which attracts the pest;
- at the currant bush, place a container with sand soaked in diesel fuel, gasoline, kerosene, or hang rags soaked in these liquids or a solution of tar in the crown of the bush (0.5 tablespoons per 5 liters of water);
- spray shrubs during the summer from the glass with infusions of pungent plants (pine, tansy, wormwood, citrus peel, onions, garlic), ammonia, vinegar.
The table describes recipes for infusions that repel pests.
Infusion | Recipe | Processing rules |
Citrus | 150 g of peels of any citrus are brewed in 1 liter of boiling water. Let it brew for 5 days in a dark cool room. | Spray currants 3 times in 10-14 days. |
Onion | 1 liter of chopped onion is steamed with 1 liter of warm water. Maintain in a closed container for 24 hours. | The bush is treated with a solution of onion tincture (20 ml per 10 l of water) when a glass case appears. |
Garlic | A medium-sized head of garlic is chopped, then 1 liter of boiled water is poured. Insist for at least a week. | Before processing, make a solution: 50 ml of tincture in 8 liters of water. Sprinkle the berry when the glass pan appears. |
Agrotechnical measures to combat currant glass
The use of correct cultivation techniques for currants, aimed at destroying the glass and its larvae, increases the effectiveness of chemical and biological insecticides and serves to prevent the spread of the pest in the backyard.
Agrotechnical measures to combat glass pan:
- The soil under and around the shrub is actively loosened during May and June. During this period, pupae appear from the larvae of the glass, which leave the internal tissues of the plant.
- Tobacco or wood ash, which has a repelling odor, is added to the soil.
- Areas of single shoots damaged by glass are pruned to healthy tissue. Completely affected branches are cut to soil level.
- If the whole plant is damaged by a pest, its sanitary pruning is carried out "to zero".
How to get rid of currant glass
In the procedures for spring and autumn currant care, it is recommended to include measures to protect against glass and other pests.
How to process currants from a glass in spring
Spring processing of currants is carried out, focusing on the years of the glass. In addition to the considered chemical and biological preparations, you can use the Antonem-F composition (200 ml per bush). They are sprayed with the crown of the bush when the buds open.
Currant cuttings are treated with the drug Nemabakt to protect against glassware before planting in the ground. To do this, they are placed for three days in sand soaked in an insecticide. The air temperature should be about 25 degrees Celsius.
How to process currants from a glass in the fall
Autumn processing of currants from the glass is a preventive measure. In addition to sanitary pruning and timely fertilization, after picking berries, you can use one of the following means:
- spray on the bushes with a 10% solution of karbofos (75 g per bucket) twice every 10 days;
- sprinkle currants with Bordeaux liquid;
- with a solution of urea (150 g per 5 l), treat the crown of the bush;
- with a pale solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate), shed the soil previously loosened around the bush;
- prepare a solution of copper sulfate (50 g per 10 l) and water the soil in the area of the trunk circle.
Resistant varieties
The currant, which is absolutely resistant to damage by glass, has not yet been selected. The following varieties of currants are characterized by the greatest endurance:
- Black: Perun, Vigorous, Summer Resident;
- White: - Dessert, Belyana, Ural white;
- Red: - Early sweet, Marmalade, Jonker Van Tets, Natalie.
More details about pest control - in the video:
Preventive actions
Preventive measures reduce the risk of damage to plants by currant glass. To prevent infection of the berry, the following measures are recommended:
- purchase of currant seedlings in specialized stores or nurseries, a thorough examination for signs of damage when purchasing planting material "from hand";
- culling cuttings with dead buds and shoots with a black hole in the center;
- regular, after 10 - 20 days, inspection and sanitary pruning of dried branches below the drying line by 4 - 5 cm;
- exclusion of mechanical damage to branches and shrub trunks;
- carrying out in the spring and autumn preventive sanitary pruning of currants with the removal of damaged, dried out shoots lying on the ground;
- disinfection and processing of cuts with garden varieties;
- examination in warm weather from October to February of currant branches: the affected shoots break when bent, they must be cut to healthy wood, in some cases - below ground level.
Conclusion
To combat currant glass, all available methods are used in aggregate: plants are treated in spring and autumn with chemical and biological means, agricultural techniques are used, and folk remedies are used. The most effective is the mechanical destruction of glass, as well as manual cutting and burning of damaged branches. It will not be possible to completely exterminate this pest in the garden, it is only possible to reduce its number.