Content
Boxwood, or buxus, as this evergreen shrub is called in Greece, has become popular everywhere. Slow growing plant is ideal for creating hedges and garden compositions. Propagating boxwood at home is a snap.
How boxwood reproduces
The shrub is propagated by cuttings, layering and seeds. This can be done in spring and autumn. Gardeners believe that autumn seedlings are easier to transplant and grow faster than spring ones.
- For the preparation of planting material, healthy strong bushes are chosen at least 2 years old.
- The soil for germination needs loose and fertile soil.
- To speed up rooting, mini greenhouses are used.
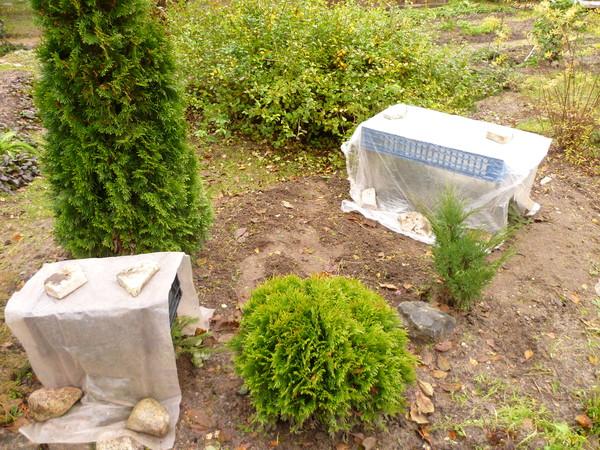
- Boxwood seedlings require shelter during the winter.
If the planting material is harvested too late, then the propagation of the plant can be carried out indoors during the cold period. In the spring, grown healthy seedlings should be planted in a permanent place in the garden.
Breeding boxwood with seeds is a more difficult method. Low germination and a long germination period often lead to failures in all attempts to reproduce shrubs from seeds, even among experienced gardeners.
How to propagate boxwood at home with cuttings
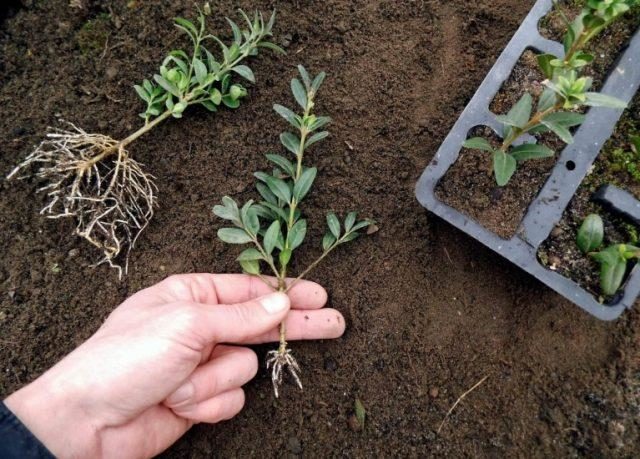
You can harvest planting material for reproduction of boxwood at home using cuttings while pruning the shrub. It is necessary to choose short, up to 15 - 20 cm, parts with intact bark. On the handle, 2 - 3 live buds must be present. It is better to cut at an angle of 45 degrees with a sharp knife.
For the stalk to take root:
- Remove bottom leaves.
- Soak in a root-forming solution according to the instructions for the preparation.
- Prepare fertile nutrient soil with a drainage layer.
- Dig in the cuttings vertically at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other.
- Drizzle with warm water and mulch the soil.
- Cover with foil or covering material.
The cuttings take about a month before the roots appear. This should be taken into account when harvesting seedlings for propagation. In the southern regions, the planting of rooted boxwood cuttings to a permanent place is carried out in late September - early October. In areas with colder climates, it is better to plant boxwood seedlings a month earlier so that the young plants have time to gain strength and do not die in winter.
During the entire period, cuttings of boxwood for propagation should be regularly watered and ventilated. It is best to do this in the evening after a decrease in solar activity.
Young plants should be planted in a chosen place along with a lump of earth so as not to damage the fragile root system.
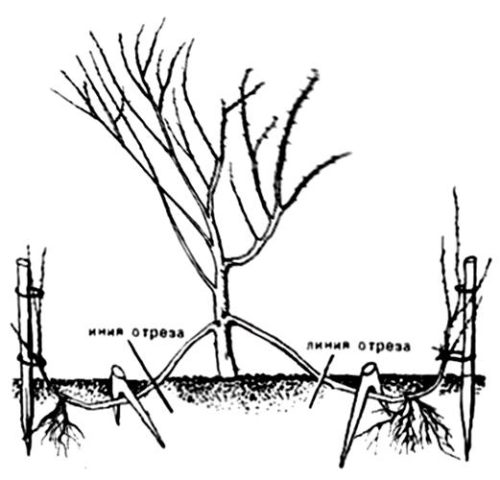
How to propagate a boxwood bush by layering
For novice gardeners, a method for propagating evergreen boxwood by layering is suitable. The procedure can be carried out at any time from spring to autumn.
For a strong, healthy boxwood shrub from two years old, you need to choose an outer branch located close to the soil surface. Then prepare a small trench up to 15 cm deep with loose fertile soil. The groove should be in the direction of the selected parent branch.
To propagate the boxwood shrub by layering, studs will be required to anchor the branch to the ground.You can use split-edged wooden pegs or bent metal wire. For the development of the root system, the branch should be cleaned of leaves and the bark should be slightly incised.
Tilt the branch, secure with pins and sprinkle with a loose soil mixture of peat, humus and sod land.
Caring for layering during reproduction consists in regular watering. The soil should not dry out. With the appearance of the first shoots, it is necessary to protect young shoots from direct sunlight.
Transplanting layers
If the sprouts from the dug-in branch have developed enough only by autumn, then it is better to leave the reproduction of the bush until spring. Before the onset of cold weather, they will have time to get stronger enough. For the winter, young shoots can be covered with the mother bush. And if the layers have grown at some distance from the adult plant, then the shelter is made of spruce or pine spruce branches.
To separate the planting material:
- Cut the mother branch from the bush with pruning shears.
- Gently dig in the soil to raise all the shoots at the same time without damaging the root system.
- Divide the seedlings with a pruner so that a small part of the mother branch remains on each. This will enable the development of additional roots.
A breeding site for boxwood must be prepared in advance. It will take a lot of skill and speed to prevent the roots from drying out. If possible, keep a lump of soil around the root system to avoid stressing the boxwood. Then the plant will quickly take root in a new place.
The soil under young plants should be moist and well fertilized. In this case, the feeding of the boxwood can be carried out one year after breeding.
To create comfortable conditions for reproduction, seedlings can be covered for a month with film caps or covering material. It is imperative to monitor the moisture content of the soil. Drying out or too much moisture will kill the plants. When breeding boxwood in the fall, it is imperative to cover the plants with layering before the onset of cold weather.
How to propagate boxwood by seeds
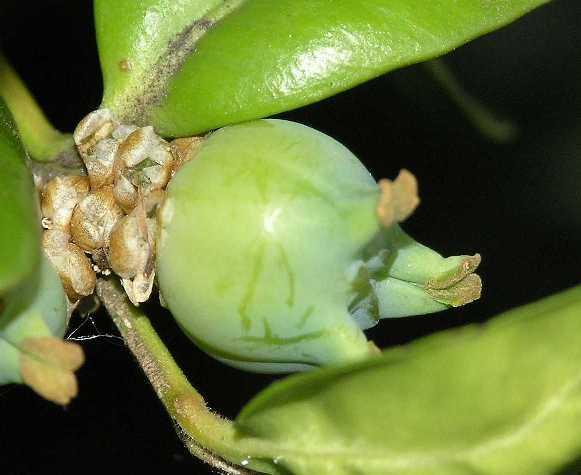
Propagating boxwood by seed can be a lot of hassle. It takes a lot of patience to collect and germinate the seed. Problems begin already when collecting seeds. Often pruned shrubs rarely have time to produce ripe seed for propagation.
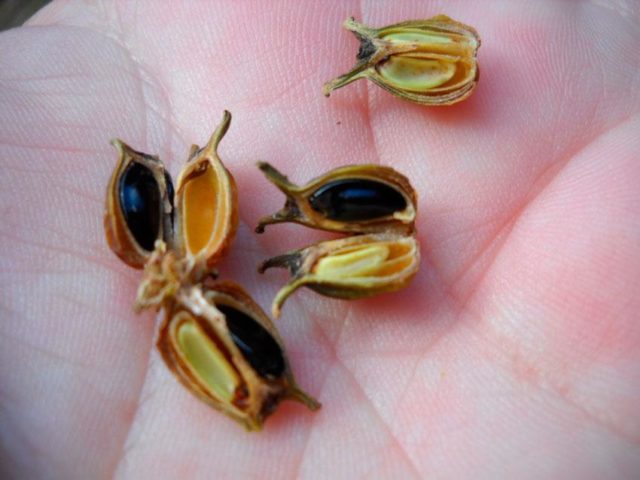
You need to collect seeds in the fall. To do this, gardeners leave branches on several bushes without cutting. Large dark achenes of boxwood are very difficult to germinate. They lose their germination as early as the next year after harvesting. If the seeds are purchased from a store, then be sure to pay attention to the date of collection. Otherwise, all the hassle of breeding boxwood will be wasted.
To soak the seeds, you will need Kornevin's solution or a similar preparation. Some gardeners use Zircon, Epin or Agricola Ecogel. Pre-planting preparation will help to increase the germination energy of seed material for propagation and increase the immunity of future seedlings.
For swelling, boxwood seeds are kept in solution for about a day. Then they need to be laid out on a dense damp cloth and covered. Germination takes at least a month. The entire period must be monitored to keep the seeds moist.
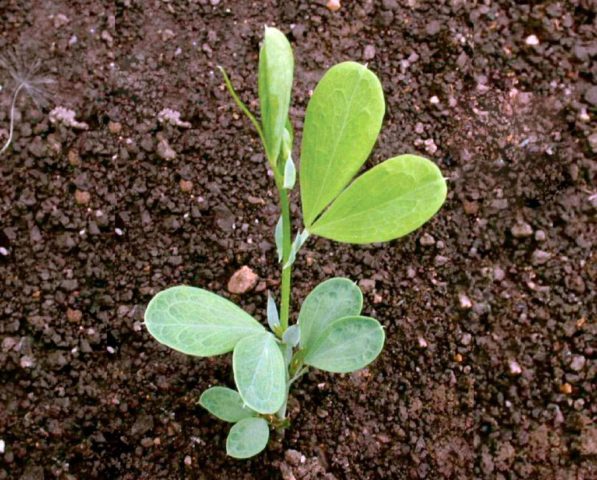
Boxwood seedlings are white. Sprouted seeds are sown with seedlings down.
To do this, you should:
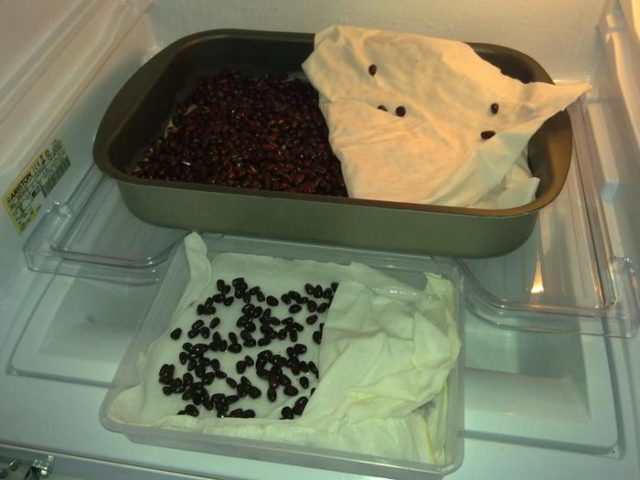
- Soak the seeds in water or a root-forming solution according to the instructions for the preparation.
- Pour a layer of sand into a small container and moisten thoroughly.
- Put the seeds at a distance of a centimeter from each other.
- Cover with a small layer of wet sand.
- Place the container on the lower shelf of the refrigerator, where the temperature is suitable for storing vegetables.
For about a month, you need to monitor so that the contents of the container with seeds do not dry out or freeze.
At the end of the term, put the container in a warm place and cover it with a plastic lid. The seeds should hatch in 3 to 4 weeks.
For sowing germinated seeds, the soil must be very loose. It is recommended to add perlite or crushed polystyrene to the soil mixture.
Place a layer of drainage mixture on the bottom of the boxwood container. You can buy it or make it yourself from charcoal, eggshells, or small pebbles. Be sure to drill holes in the bottom to remove excess water when watering.
The soil for planting seeds must be prepared in advance. If the soil mixture was made independently, then it is important to warm it up or treat it with antifungal drugs for disinfection.
It is better to sow seeds one at a time in small containers. This method is not too economical, but it allows you not to touch young boxwood seedlings for a long time.
If the root system of the plant has completely filled the container, and it is still far away from planting to a permanent place, then the seedlings need to be transplanted into large pots by transshipment.
- Partially fill the new container with soil, having previously laid the drainage.
- Water the plant abundantly.
- Carefully remove the seedling along with a clod of earth.
- Place in a new pot.
- Add soil in diameter, slightly compacting it.
Further work on the reproduction of boxwood by seeds consists in regular watering and fertilization. The first feeding should be done one month after the sprouts appear. For this, it is better to use complex mineral preparations. In the future, you can fertilize the plants after 2 - 2.5 weeks.
With the onset of heat, containers with seedlings can be placed in a greenhouse or a place protected from wind and sunlight for hardening.
It is better to plant boxwood obtained from seeds in open ground at the end of August. Before the cold weather, young seedlings will have time to get stronger and develop a root system.
It is important to remember that for wintering it is necessary to mulch the soil under the bushes with a thick layer of peat or rotted compost or manure.
Sometimes it is just enough to breed boxwood with seeds. Some rare varieties of this evergreen shrub are too expensive. Growing them by cuttings or layering can take too long due to the slow growth of the shrub.
An alternative breeding method for boxwood
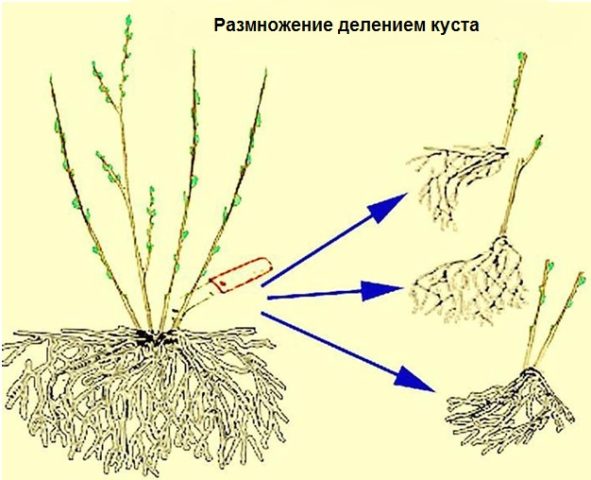
Sometimes gardeners are forced to resort to dividing boxwood bushes. Old bushes, even with careful pruning, end up filling the allotted space. With a lack of light and nutrition, the overgrown branches lose their decorative effect.
By dividing the bush, you can plant boxwood in the garden. You can transplant at any time from spring to autumn. To do this, you need to dig up the soil from the side where you plan to separate a part of the plant. Cut off a part of the root with several healthy shoots with a sharp shovel or knife.
Place the seedling strictly vertically in the prepared planting hole with nutritious soil. Lay the soil, gradually compacting it. It is desirable that the soil is moist. This will avoid creating voids around the root system. New seedlings should be watered regularly and fed like mature plants. In the first days after planting, the culture must be protected from direct sunlight.
Conclusion
To propagate boxwood on your own is within the power of a beginner. The evergreen shrub looks very beautiful in group plantings and hedges. But do not forget that boxwood is a poisonous plant, and if the juice of the leaves gets on the skin or inside, negative consequences can occur.